Turboprop Engine Market Developments Drive Advancements in Fuel Efficiency and Digital Integration
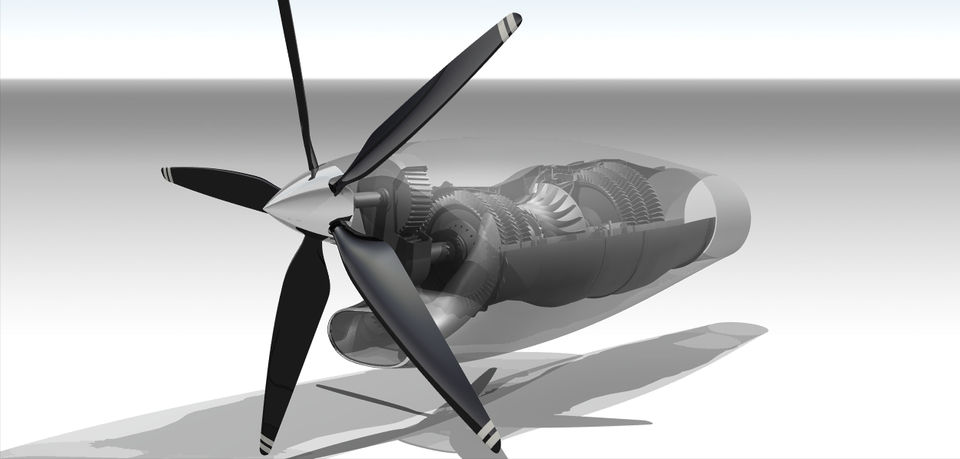
The turboprop engine market has seen a wave of innovation over the past decade, driven by evolving aviation needs, advancements in technology, and increasing environmental awareness. While turboprop engines have long been valued for their fuel efficiency and performance at low to medium altitudes, recent innovations are making them more competitive, sustainable, and versatile for various aerospace applications. From hybrid propulsion systems to advanced materials and digital integration, the turboprop engine market is transforming to meet future challenges and opportunities.
Hybrid-Electric Propulsion: Redefining Power Sources
One of the most transformative innovations in the turboprop engine space is the integration of hybrid-electric propulsion systems. Aircraft manufacturers and engine developers are exploring the blending of traditional fuel-based engines with electric motors to improve fuel efficiency, reduce emissions, and support quieter operations. These hybrid systems are particularly suitable for regional and short-haul flights, where turboprops already excel. Companies like Pratt & Whitney Canada are investing heavily in research to develop hybrid-electric turboprop demonstrators, signaling a new direction for the market.
Sustainable Aviation Fuel (SAF) Compatibility
Another major innovation lies in making turboprop engines compatible with sustainable aviation fuels (SAFs). These bio-based or synthetic fuels have a significantly lower carbon footprint compared to traditional jet fuels. Many modern turboprop engines, such as the GE Catalyst and PW100 series, are now being certified for use with SAFs. This shift supports broader industry goals of achieving net-zero emissions by 2050 and aligns turboprop engines with global sustainability initiatives.
Advanced Materials and Lightweight Components
To improve engine performance and reduce operational costs, manufacturers are adopting advanced materials such as ceramic matrix composites, carbon fiber-reinforced plastics, and titanium alloys. These materials are not only lighter than traditional metal components but also offer higher heat resistance and durability. Reducing engine weight leads to better fuel economy and enhances the payload capability of aircraft, which is critical in the highly cost-sensitive regional aviation sector.
Digital Twin Technology and Predictive Maintenance
Digital transformation is another area revolutionizing turboprop engines. The implementation of digital twin technology—a virtual replica of a physical engine—allows engineers and maintenance crews to monitor engine health in real time. This technology uses data analytics, AI, and IoT sensors to predict potential failures, optimize maintenance schedules, and minimize downtime. Predictive maintenance reduces operational disruptions and enhances the lifecycle performance of turboprop engines.
Modular Engine Design for Versatility
Innovations in engine architecture, particularly modular design, are making turboprop engines more adaptable and easier to maintain. Modular designs enable easier replacement of individual parts or subsystems, reducing maintenance time and cost. This flexibility is beneficial in both civil and military aviation sectors, especially for operators in remote areas or challenging environments where logistical support may be limited.
Noise Reduction Technologies
With increasing regulatory pressure and community concerns over airport noise pollution, reducing the acoustic footprint of turboprop engines is gaining attention. New propeller blade designs, variable pitch mechanisms, and engine casing improvements are being implemented to lower noise levels. Some turboprop engines are now as quiet as comparable regional jets, making them more attractive for urban and regional routes.
Autonomous and Unmanned Applications
Turboprop engines are also being integrated into autonomous and unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) due to their efficiency, endurance, and reliability. This application is growing in both defense and commercial sectors, including cargo delivery, surveillance, and environmental monitoring. Innovations are focused on adapting turboprop systems for UAV platforms, including lightweight and modular designs, improved fuel efficiency, and seamless integration with AI navigation systems.
Conclusion
The turboprop engine market is undergoing a renaissance driven by a convergence of technological, environmental, and operational imperatives. Innovations in hybrid propulsion, sustainable fuels, advanced materials, digital systems, and UAV integration are positioning turboprops as engines of the future—capable of serving traditional roles while expanding into new frontiers. As the aviation industry pivots toward sustainability and cost-efficiency, turboprop engines will likely remain a key part of the equation, evolving to meet the demands of a changing world.
- Art
- Causes
- Crafts
- Dance
- Drinks
- Film
- Fitness
- Food
- Games
- Gardening
- Health
- Home
- Literature
- Music
- Networking
- Other
- Party
- Religion
- Shopping
- Sports
- Theater
- Wellness
- Politics
- IT
- Relationship
- Blockchain
- NFT
- Crypto
- Fintech
- Automobile
- Faith
- Family
- Animals
- Travel
- Pets
- Coding
- Comedy
- Movie
- Game
- Computer



