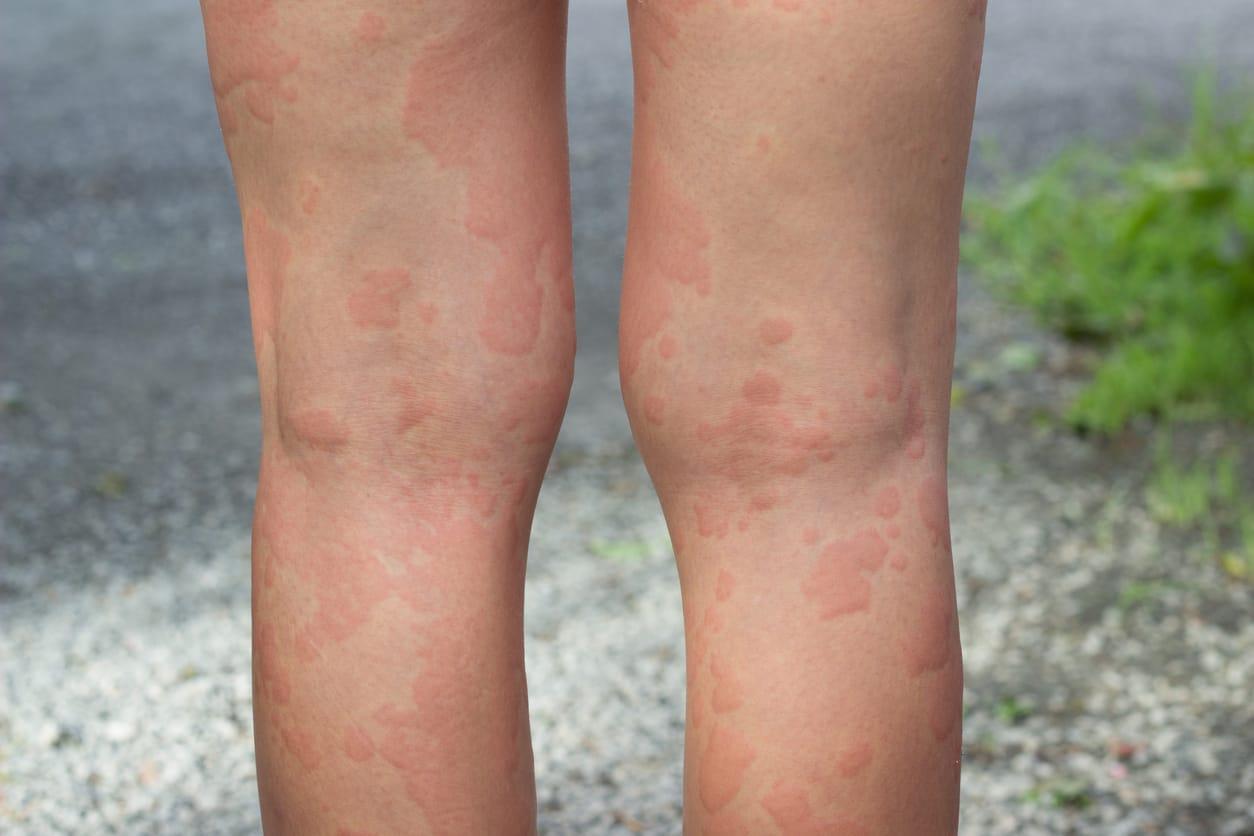
Chronic hives, also known as chronic urticaria, can be a frustrating and disruptive condition that affects daily life. Unlike acute hives that resolve within a few hours or days, chronic hives persist for six weeks or more and may recur for months or even years. Hives Specialists are experts in diagnosing and treating this condition, helping patients find effective, long-term relief.
If you are experiencing frequent or persistent hives, a Hives Specialist can identify triggers, provide advanced treatment options, and develop a customized management plan. This blog explores how these specialists help patients overcome chronic urticaria.
What Are Chronic Hives?
Chronic hives are characterized by raised, red, itchy welts on the skin that last for extended periods. They can appear anywhere on the body and often occur unpredictably. In some cases, chronic hives are accompanied by swelling in deeper skin layers, known as angioedema.
Causes of Chronic Hives
The exact cause of chronic hives is often unknown, but common factors include:
-
Autoimmune disorders – The immune system mistakenly attacks healthy cells.
-
Infections – Viral, bacterial, or parasitic infections can trigger hives.
-
Allergies – Some cases are linked to food, medications, or environmental allergens.
-
Hormonal changes – Fluctuations in hormones may contribute to flare-ups.
-
Stress and anxiety – Emotional triggers can worsen symptoms.
Symptoms of Chronic Hives
-
Persistent, itchy, red, or skin-colored welts
-
Welts that change shape, size, and location
-
Swelling (angioedema) in the lips, eyelids, hands, or feet
-
Burning or stinging sensations
-
Symptoms that last for months or years
How Hives Specialists Diagnose Chronic Urticaria
1. Patient History and Symptom Assessment
A Hives Specialist will ask about the frequency, duration, and severity of symptoms, along with lifestyle and environmental factors that may contribute to outbreaks.
2. Allergy and Blood Tests
-
Skin prick tests – Identify potential allergens.
-
Blood tests – Rule out underlying infections or autoimmune conditions.
3. Autoimmune Screening
Since chronic hives can be linked to autoimmune disorders like lupus or thyroid disease, specialists may conduct tests for these conditions.
4. Challenge Tests
For cases suspected to be triggered by cold, heat, or pressure, specialists may perform physical challenge tests.
Treatment Strategies Used by Hives Specialists
1. Non-Drowsy Antihistamines
The first-line treatment for chronic hives includes second-generation antihistamines like:
-
Cetirizine
-
Fexofenadine
-
Loratadine
2. Higher-Dose or Combined Antihistamine Therapy
In severe cases, specialists may increase antihistamine doses or combine different types for better symptom control.
3. Corticosteroids
Short-term corticosteroid use helps reduce inflammation for severe flare-ups, but long-term use is avoided due to side effects.
4. Biologic Therapy (Omalizumab/Xolair)
This injectable medication blocks the immune system’s response, providing effective relief for chronic hives that don’t respond to antihistamines.
5. Immunosuppressants
For autoimmune-related hives, medications like cyclosporine or methotrexate may be prescribed.
6. Identifying and Avoiding Triggers
-
Maintaining a food and symptom diary
-
Avoiding environmental allergens
-
Managing stress through relaxation techniques
7. Home Remedies & Self-Care
-
Applying cool compresses to affected areas
-
Wearing loose, cotton clothing to reduce irritation
-
Using mild, fragrance-free skincare products
When Should You See a Hives Specialist?
-
If hives persist for more than six weeks
-
If symptoms interfere with daily life or sleep
-
If over-the-counter treatments do not provide relief
-
If you experience swelling in the throat or difficulty breathing (emergency situation)
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. Can chronic hives be cured?
There is no permanent cure, but effective treatments can help manage and reduce symptoms.
2. What is the most effective treatment for chronic hives?
A combination of antihistamines, biologic therapy, and trigger avoidance provides the best results.
3. Are chronic hives a sign of an autoimmune disease?
Yes, in some cases, chronic hives are linked to autoimmune disorders like lupus or thyroid disease.
4. Can stress make chronic hives worse?
Yes, stress and anxiety can trigger or worsen symptoms in some individuals.
5. How can I prevent chronic hives from flaring up?
Identifying and avoiding triggers, maintaining a healthy lifestyle, and following a specialist’s treatment plan can help prevent flare-ups.
If you are dealing with persistent hives, consulting a Hives Specialist is the best way to find relief and regain control over your symptoms.