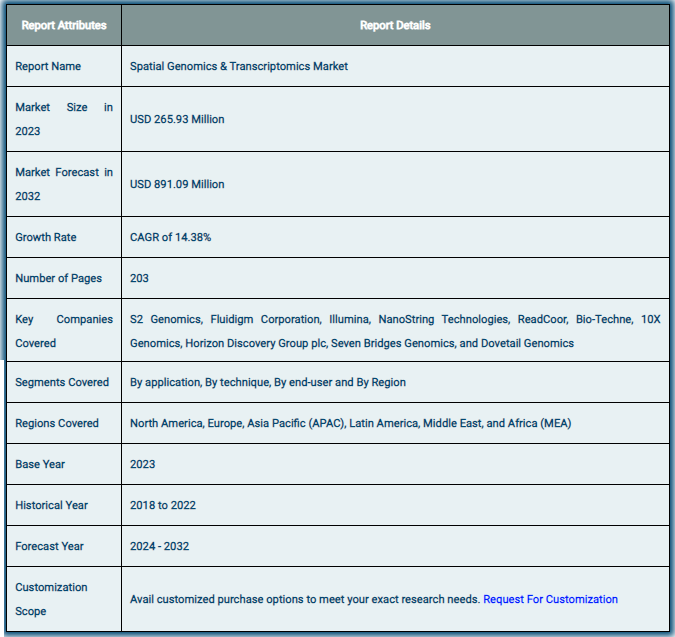
The global market for spatial genomics and transcriptomics was estimated to be worth USD 265.93 million in 2024 and is expected to grow to USD 891.09 million by the end of 2032, according to a report released by Zion Market Research. Over the course of the projection period, the market is anticipated to expand at a CAGR of 14.38%. The study examines the factors that will propel growth, impede it, and affect demand in the global spatial genomics and transcriptomics market over the course of the projected year. Additionally, it will support you as you navigate and investigate the new opportunities in the transcriptomics and spatial genomics sector.
Introduction
Spatial genomics and transcriptomics represent cutting-edge areas of biotechnology, providing deep insights into the spatial organization of gene expression within tissues. By preserving the spatial context of biological data, these technologies offer researchers unprecedented opportunities to study cellular heterogeneity, tissue architecture, and disease mechanisms. As these technologies continue to advance, the spatial genomics and transcriptomics market is poised for significant growth, driven by increasing demand from academic research institutions, pharmaceutical companies, and clinical laboratories.
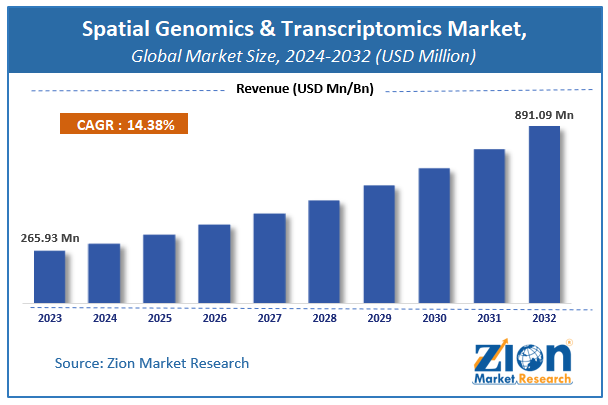
Overview of the Global Market for Spatial Genomics and Transcriptomics
The healthcare industry is undergoing a transformation thanks to technical developments in medical research and technology. By using this technology, one may spatially resolve RNA sequencing data and, consequently, mRNAs in tissue sections from a person. Selecting the desired gene and displaying its spatially resolved expression on a portion of the original tissue is made possible by the data produced by spatial transcriptomics technology. Since every mRNA is recorded, scientists and researchers are not limited to seeing just one gene. It is possible to select any number of genes to view and examine collectively.
Growth Factors for the Global Spatial Genomics and Transcriptomics Market
The global market for spatial genomics and transcriptomics is expanding as a result of factors such as the rise in biomarker identification using spatial omics, the increased focus of biopharmaceuticals and biotech companies on novel drug discovery & development programs, and the rise in adoption of these technologies by small and startup businesses. In order to evaluate homeostasis, cellular function, and changes in gene expression, information gleaned from the genetic components of the cells — such as the chromatin network, RNA, and DNA — is essential. This information is also connected with the progression and stages of disease.
On the other hand, nothing is known about the transcriptome and genomic level of localisation, differentiation, and spatial organisation of the tissue and cells. When using traditional methods, this kind of data is not properly obtained, leading to the loss of important details on the cellular machinery. Spatial genomics and transcriptomics are fields of study that are fast evolving to close this knowledge gap. Consequently, there is a great need for transcriptomics and spatial genomics, which is driving the global market’s expansion. Additionally, the market is expanding due to the rising need for spatial genomics and transcriptomics in clinical development and research in fields like immunology, neurology, cardiovascular disease, and infectious disease.
Additionally, the introduction of multiplexed, high-throughput systems and fluorescence in situ hybridisation (FISH) technology will create significant prospects for the expansion of the worldwide market for spatial genomics and transcriptomics. However, the global market for spatial genomics and transcriptomics may not grow as quickly as it could due to a shortage of qualified workers.
The global market for transcriptomics and spatial genomics has been moderately impacted by the Covid-19 epidemic. When the Covid-19 first started to spread, the government’s severe lockdown and mobility restrictions caused a disturbance in the supply chain and made personnel unavailable. The supply of consumables, instruments, and reagents has been impacted by these issues. Furthermore, academic institutions and research have closed, which has significantly affected the need for analysis utilising transcriptomics and spatial genomics. However, because of the growing importance of biomarker identification and its application in drug development and discovery initiatives, the global market for spatial genomics and transcriptomics is anticipated to expand at a healthy pace in the future years.

Market Segmentation for Global Spatial Genomics and Transcriptomics
There are four segments in the global market for spatial genomics and transcriptomics: application, technology, end-user, and region.
The global market for spatial genomics and transcriptomics is segmented into two segments based on the application: medication discovery and development and translational research.
The global market is divided into three segments based on the technique: product, spatial transcriptomics, and spatial genomic analysis.
Academic & research institutes, contract research organisations, and pharmaceutical & biotech corporations make up the end-user category.
Market Analysis: Spatial Genomics & Transcriptomics: Report Summary
Regional Analysis of the Global Spatial Genomics & Transcriptomics Market
The largest market share in the worldwide spatial genomics and transcriptomics market is anticipated to reside in North America. The fast adoption of cutting-edge technology, the rise in demand from academic and research institutions, and the presence of major companies are all factors driving the market’s expansion in this area. Due to the existence of both new businesses and a well-established healthcare infrastructure, Europe is the second-largest market. Due to a growth in drug discovery and development initiatives and the number of contract research organisations providing services to research institutes and the pharmaceutical industry, the market in Asia Pacific is predicted to grow at a quicker rate.
Key Market Trends
- Rising Adoption of Single-Cell Analysis: The integration of single-cell analysis with spatial genomics and transcriptomics is a major trend driving market growth. Single-cell technologies allow researchers to examine gene expression at an individual cell level, offering valuable insights into cellular diversity and disease progression. When combined with spatial analysis, these techniques enable a more comprehensive understanding of tissue biology, which is critical for cancer research, neuroscience, and regenerative medicine.
- Advancements in Imaging and Sequencing Technologies: Technological advancements in imaging and sequencing are propelling the spatial genomics and transcriptomics market forward. High-resolution imaging techniques, such as fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) and multiplexed error-robust fluorescence in situ hybridization (MERFISH), allow for the precise localization of gene expression. Meanwhile, next-generation sequencing (NGS) continues to evolve, offering higher throughput and greater accuracy. These advancements are expanding the capabilities of spatial genomics and transcriptomics, making them more accessible to a wider range of researchers.
- Integration with Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning: Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) are increasingly being integrated into spatial genomics and transcriptomics workflows. AI-driven algorithms are used to analyze complex datasets, identify patterns, and predict biological outcomes. This integration is particularly valuable in processing large-scale spatial data, enabling faster and more accurate interpretation of results. As AI and ML continue to evolve, their role in spatial genomics and transcriptomics is expected to grow, further enhancing the efficiency and scalability of these technologies.
- Growing Interest in Disease Mechanisms and Drug Development: Spatial genomics and transcriptomics are playing a crucial role in unraveling the mechanisms of complex diseases, such as cancer, Alzheimer’s, and autoimmune disorders. By preserving the spatial context of gene expression, researchers can gain insights into how diseases progress and identify potential therapeutic targets. Pharmaceutical companies are leveraging these technologies in drug discovery and development, using spatial data to assess drug efficacy and toxicity at the tissue level.
- Expansion of Clinical Applications: While spatial genomics and transcriptomics have primarily been used in basic research, their clinical applications are rapidly expanding. In oncology, for example, spatial transcriptomics is being used to identify biomarkers for personalized medicine, allowing for more precise and targeted treatments. Additionally, spatial genomics is being explored for use in diagnostics, particularly in complex diseases where traditional methods fall short. As these technologies become more refined and cost-effective, their adoption in clinical settings is expected to rise.
Growth Drivers
- Increased Funding and Investments: The spatial genomics and transcriptomics market is benefiting from increased funding and investments from both public and private sectors. Governments and research institutions are recognizing the potential of these technologies to drive innovation in biomedical research, leading to significant investments in infrastructure and technology development. Additionally, venture capital firms are investing in startups specializing in spatial genomics and transcriptomics, fueling market growth.
- Collaborations and Partnerships: Strategic collaborations between academic institutions, research organizations, and industry players are driving the development of new spatial genomics and transcriptomics technologies. These partnerships facilitate the exchange of knowledge, resources, and expertise, accelerating innovation and commercialization. Collaborations are also helping to bridge the gap between research and clinical applications, enabling faster translation of discoveries into therapies.
- Rising Demand for Personalized Medicine: The growing demand for personalized medicine is a major driver of the spatial genomics and transcriptomics market. As healthcare shifts towards more individualized treatments, there is a need for technologies that can provide detailed molecular insights at the tissue level. Spatial genomics and transcriptomics offer the ability to map gene expression in situ, providing critical information for tailoring treatments to individual patients.
- Technological Advancements: Continuous advancements in technology are making spatial genomics and transcriptomics more accessible and affordable. Innovations in sequencing, imaging, and data analysis are reducing the cost and complexity of these techniques, enabling broader adoption across various research and clinical settings.
Challenges Facing the Market
- High Costs and Technical Complexity: Despite technological advancements, the high costs and technical complexity of spatial genomics and transcriptomics remain significant barriers to widespread adoption. These technologies require specialized equipment, expertise, and computational resources, which can be prohibitively expensive for smaller laboratories and institutions. Addressing these challenges will be critical for scaling the market.
- Data Management and Interpretation: The vast amounts of data generated by spatial genomics and transcriptomics present challenges in terms of storage, management, and interpretation. Researchers need robust bioinformatics tools and infrastructure to handle and analyze large datasets. Additionally, the complexity of spatial data requires specialized expertise to draw meaningful conclusions, which can be a limiting factor for some organizations.
- Standardization and Reproducibility: As spatial genomics and transcriptomics technologies are still relatively new, there is a lack of standardization in methodologies and protocols. This can lead to variability in results and challenges in reproducing findings across different laboratories. Establishing standardized protocols and best practices will be essential for ensuring consistency and reliability in the field.
- Regulatory and Ethical Considerations: As spatial genomics and transcriptomics move closer to clinical applications, regulatory and ethical considerations will become increasingly important. Ensuring patient privacy, data security, and compliance with regulatory frameworks will be critical for the successful integration of these technologies into clinical practice.
Future Outlook
The spatial genomics and transcriptomics market is poised for substantial growth in the coming years, driven by ongoing technological advancements, increasing demand for personalized medicine, and expanding clinical applications. As the market continues to evolve, key players will need to address challenges related to cost, complexity, and standardization to fully capitalize on the opportunities in this space.
In conclusion, spatial genomics and transcriptomics represent a transformative area of biotechnology with the potential to revolutionize our understanding of biology and disease. By providing spatial context to gene expression data, these technologies are opening new avenues for research, diagnostics, and therapeutics. As the market continues to mature, we can expect to see even greater integration of spatial genomics and transcriptomics into the broader biomedical landscape.
Contact Us:
Zion Market Research212
USA/Canada Toll Free: 1 (855) 465–4651
Newark: 1 (302) 444–016611\s
Web: https://www.zionmarketresearch.com/
Blog: https://zmrblog.com/
Browse other trend reports:
https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/digital-insurance-platform-market-size-share-trends-kirue
https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/business-management-consulting-service-market-size-i0qle
https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/spatial-genomics-transcriptomics-market-size-share-hamke
https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/machine-learning-service-market-size-share-industry-sxjke
https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/mobile-apps-web-analytics-market-size-share-industry-slsae
